Understanding the Product Life Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: In the dynamic landscape of business, every product goes through a series of stages known as the Product Life Cycle (PLC). Understanding this cycle is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions regarding their products. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the Product Life Cycle, its stages, and strategies for each stage.
What is the Product Life Cycle?
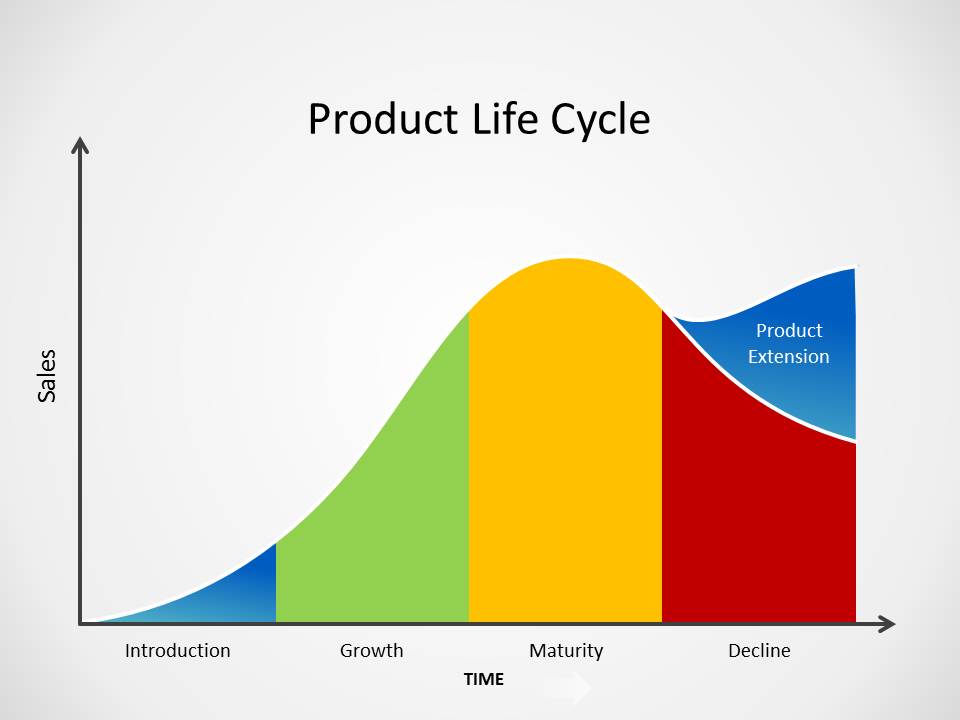
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a concept that describes the stages a product goes through from its introduction to its decline in the market. These stages typically include Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline.
Stage 1: Introduction
During the introduction stage, a product is launched into the market. Sales are typically low as consumers become aware of the product and its benefits. Companies often invest heavily in marketing and promotion to create product awareness.
Stage 2: Growth
In the growth stage, the product experiences rapid sales growth as consumer demand increases. Competition may also intensify during this stage as more competitors enter the market. Companies focus on expanding market share and enhancing product features.
Stage 3: Maturity
The maturity stage is characterized by stable sales and market saturation. Competitors may offer similar products, leading to price competition. Companies may innovate by introducing product variations or focusing on cost reduction to maintain profitability.
Stage 4: Decline
During the decline stage, sales start to decline as consumer preferences shift or new technologies emerge. Companies may choose to discontinue the product or revitalize it through repositioning or product innovation.
Strategies for Each Stage:
Introduction Stage: Focus on building product awareness and creating a strong brand identity. Invest in marketing and promotion to attract early adopters.
Growth Stage: Expand distribution channels and invest in product development to capitalize on increasing demand. Maintain competitive pricing to maximize market share.
Maturity Stage: Differentiate the product through branding or product features to sustain market share. Explore new markets or customer segments to prolong the product life cycle.
Decline Stage: Consider product diversification or product line extensions to mitigate sales decline. Evaluate the feasibility of repositioning the product or discontinuing it.















Case Studies:
Introduction Stage: Apple's launch of the iPhone revolutionized the smartphone industry, creating significant buzz and anticipation among consumers.
Growth Stage: Netflix experienced rapid growth during the early 2000s as streaming technology became more accessible, leading to a shift away from traditional DVD rentals.
Maturity Stage: Coca-Cola has maintained market dominance for decades by continuously innovating its product offerings and expanding into new markets worldwide.
Decline Stage: BlackBerry, once a leader in the smartphone market, faced declining sales due to competition from iOS and Android devices, ultimately leading to a decline in market share.
Conclusion:
The Product Life Cycle is a fundamental concept that guides businesses in managing their product portfolios effectively. By understanding each stage of the PLC and implementing appropriate strategies, companies can prolong the life of their products and remain competitive in ever-changing markets. Embracing innovation and adaptation is key to navigating the complexities of the Product Life Cycle and achieving long-term success.
Comments
Post a Comment