Understanding the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix: A Strategic Analysis Tool
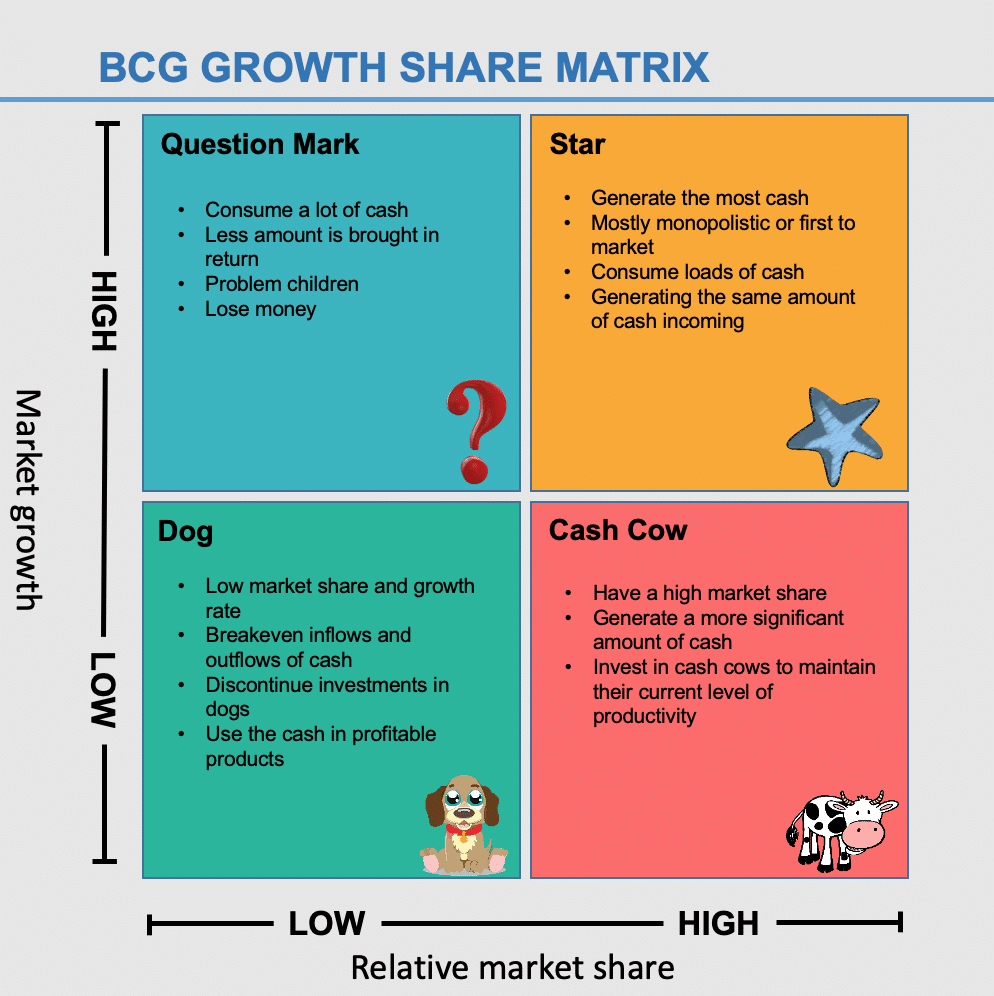

- Stars represent products or services with high market share in a rapidly growing market.
- These products require significant investment to maintain their competitive position and sustain growth.
- As the market matures, stars have the potential to become cash cows.
- Cash cows are products or services with high market share in a low-growth market.
- These products generate substantial cash flow but require minimal investment for maintenance.
- Cash cows are typically mature products that have already captured a significant market share.
- Question marks are products or services with low market share in a high-growth market.
- These products require investment to capture market share and become stars.
- Question marks may either become stars if investment leads to growth or may be divested if growth prospects are low.
- Dogs represent products or services with low market share in a low-growth market.
- These products have limited growth prospects and may consume resources without generating significant returns.
- Dogs may be candidates for divestiture or restructuring to minimize losses.
Company XYZ manufactures a range of electronic products, including smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. Using the BCG Matrix, the company categorizes its products as follows:
Smartphones: With a dominant market share and high growth rate in the rapidly evolving smartphone market, the company's smartphones are categorized as stars. To maintain their competitive position, the company invests heavily in research and development, marketing, and innovation to introduce new features and models.
Tablets: While the tablet market is growing at a slower pace compared to smartphones, Company XYZ holds a significant market share with its range of tablets. These products are classified as cash cows, generating steady cash flow with minimal investment required for maintenance.
Smartwatches: In the emerging market for wearable technology, Company XYZ's smartwatches have yet to gain significant market share. However, the market shows potential for growth. These products are classified as question marks, requiring additional investment to capture market share and establish themselves as stars.
Digital Cameras: With declining demand and increasing competition from smartphones with advanced camera capabilities, Company XYZ's digital cameras have a low market share in a declining market. These products are classified as dogs, requiring strategic decisions such as divestiture or restructuring to minimize losses.

Comments
Post a Comment