Understanding the McKinsey 7-S Framework: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Introduction: The McKinsey 7-S Framework is a management model developed by consulting firm McKinsey & Company to help organizations analyze and align their internal elements for effective performance. This framework identifies seven interconnected factors that are critical for organizational success. In this blog post, we will explore each element of the McKinsey 7-S Framework in tabular format, accompanied by examples to illustrate their application.
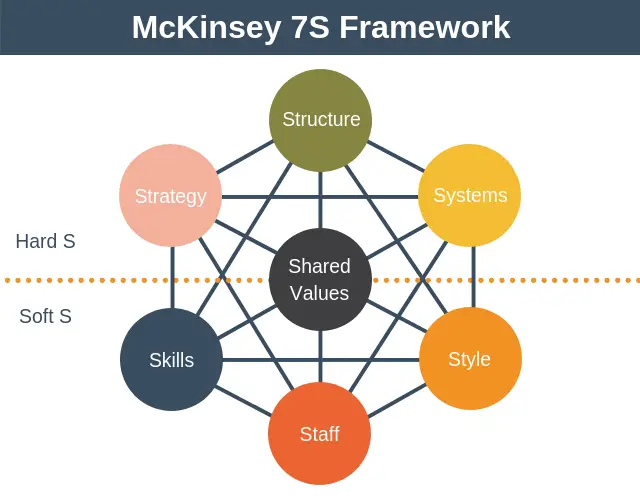
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | The overarching plan to achieve goals | Developing a market expansion strategy |
| Structure | The organization's hierarchy and design | Centralized vs. decentralized structure |
| Systems | Processes and procedures for operations | Implementing a new CRM system |
| Shared Values | Core beliefs and principles | Commitment to customer satisfaction |
| Skills | Competencies and capabilities | Technical skills in software development |
| Style | Leadership and management approach | Participative vs. authoritative leadership |
| Staff | Human resources and talent | Hiring employees with diverse skill sets |
Strategy:
- Description: Strategy refers to the organization's plan for achieving its goals and objectives.
- Example: Developing a market expansion strategy to enter new geographic markets and target customer segments.
Structure:
- Description: Structure encompasses the organization's hierarchy, reporting lines, and decision-making processes.
- Example: Choosing between a centralized or decentralized organizational structure based on the organization's size and complexity.
Systems:
- Description: Systems include the processes, procedures, and workflows that govern how work is performed within the organization.
- Example: Implementing a new Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to streamline sales and customer interactions.
Shared Values:
- Description: Shared values represent the core beliefs and principles that guide behavior and decision-making within the organization.
- Example: A commitment to customer satisfaction as a core value driving all business decisions and actions.
Skills:
- Description: Skills refer to the competencies and capabilities possessed by employees to perform their roles effectively.
- Example: Technical skills in software development, including programming languages and coding proficiency.
Style:
- Description: Style relates to the leadership and management approach adopted within the organization.
- Example: Leadership style characterized by participative decision-making and employee empowerment, fostering a collaborative work environment.
Staff:
- Description: Staff encompasses the human resources and talent within the organization, including recruitment, training, and development.
- Example: Hiring employees with diverse skill sets and backgrounds to foster innovation and creativity within the organization.
Conclusion:
The McKinsey 7-S Framework provides a comprehensive framework for analyzing and aligning key elements within an organization to drive effective performance. By considering the interplay between strategy, structure, systems, shared values, skills, style, and staff, organizations can better understand their internal dynamics and make strategic decisions to achieve their goals. Through the examples provided, we have demonstrated how each element of the 7-S Framework can be applied in real-world contexts to enhance organizational effectiveness and success.
Comments
Post a Comment