Unleashing the Power of Marketing Analytics: Leveraging Data for Strategic Decision Making
In today's digital era, data has become the lifeblood of marketing, providing valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and fuel business growth. Marketing analytics, the practice of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to optimize marketing efforts, has emerged as a critical discipline for businesses seeking to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the importance of marketing analytics, its key components, and how businesses can leverage data to make informed and impactful marketing decisions.
Part 1: Understanding Marketing Analytics
1.1 What is Marketing Analytics?
- Marketing analytics involves the process of collecting, measuring, analyzing, and interpreting data related to marketing activities and performance.
- It encompasses various data sources, including website analytics, social media metrics, email campaign data, customer demographics, and sales data.
1.2 Importance of Marketing Analytics:
- Data-driven Decision Making: Marketing analytics empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on quantitative insights rather than intuition or guesswork.
- Optimization and Efficiency: By analyzing marketing performance data, businesses can identify areas of strength and weakness, optimize campaigns, and allocate resources more efficiently.
- Customer Understanding: Marketing analytics provides valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs, enabling businesses to tailor marketing efforts to specific audience segments.
Part 2: Key Components of Marketing Analytics
2.1 Data Collection:
- The first step in marketing analytics is collecting relevant data from various sources, including website analytics platforms (e.g., Google Analytics), social media channels, email marketing platforms, CRM systems, and third-party data providers.
- Data collection should be comprehensive, capturing both online and offline interactions, customer touchpoints, and key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to marketing goals.
2.2 Data Analysis:

- Once data is collected, it must be analyzed to extract actionable insights and identify trends, patterns, and correlations.
- Data analysis techniques may include descriptive analytics (summarizing historical data), diagnostic analytics (identifying root causes of performance issues), predictive analytics (forecasting future trends), and prescriptive analytics (providing recommendations for action).
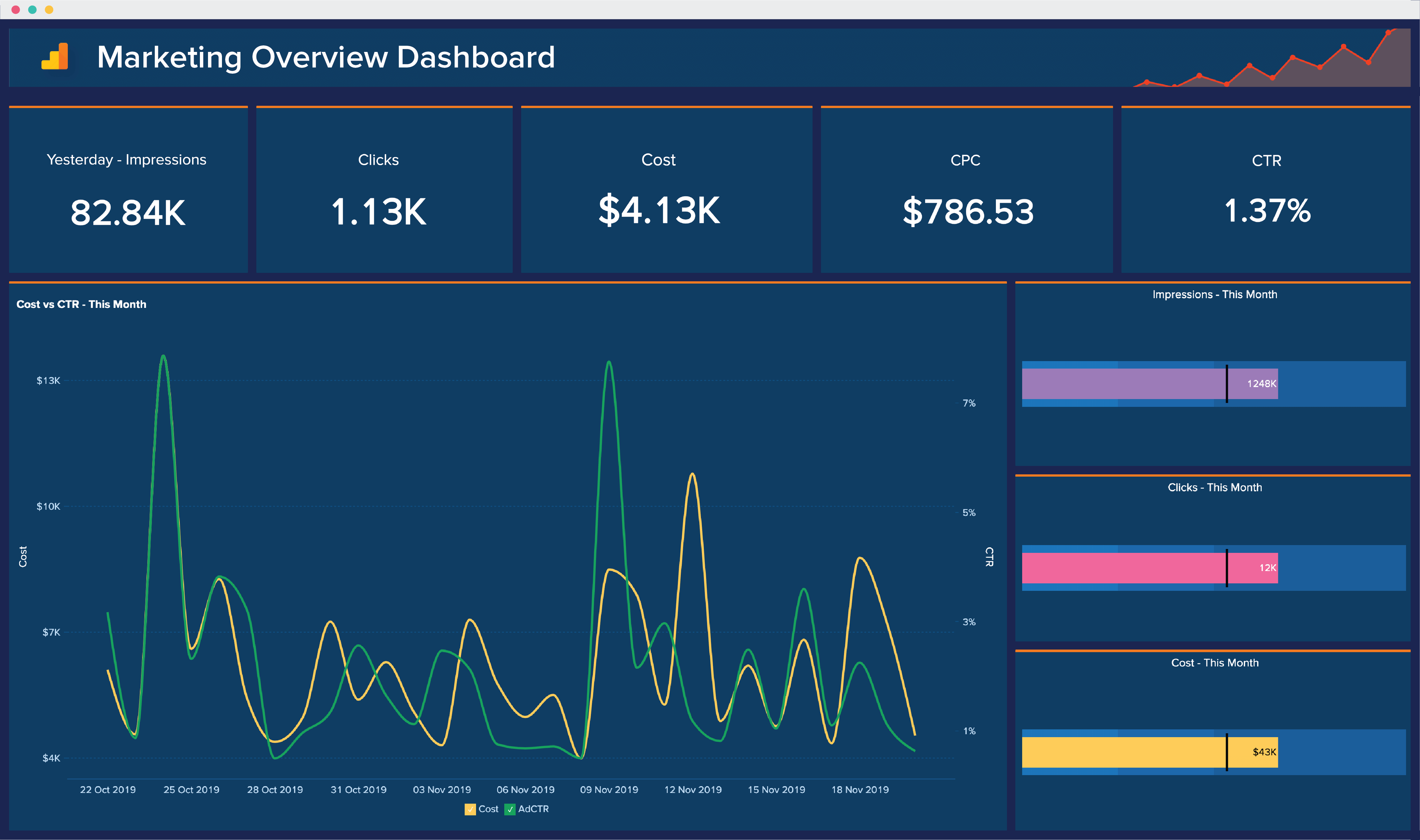
2.3 Visualization and Reporting:
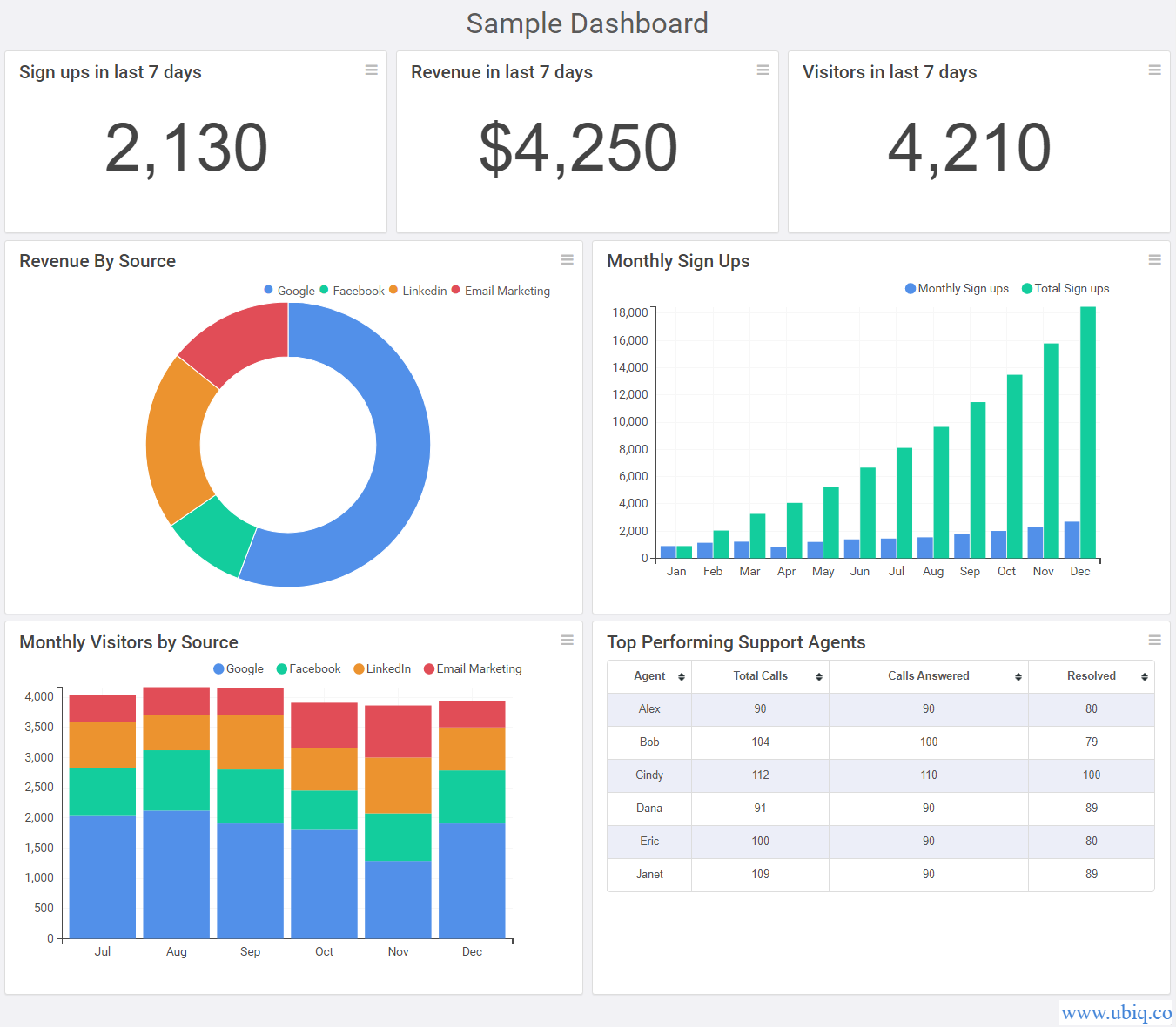
- Data visualization tools and dashboards play a crucial role in presenting marketing analytics findings in a clear, concise, and visually compelling manner.
- Visualizations such as charts, graphs, heatmaps, and dashboards help stakeholders understand complex data sets, track KPIs, and monitor performance metrics in real-time.
Part 3: Leveraging Data for Strategic Decision Making
3.1 Audience Segmentation:
- Marketing analytics enables businesses to segment their audience based on demographic, psychographic, and behavioral attributes.
- By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different audience segments, businesses can tailor marketing messages, offers, and channels to maximize relevance and engagement.
3.2 Campaign Optimization:
- Analyzing campaign performance data allows businesses to identify which marketing channels, messages, and tactics are driving the highest ROI.
- Businesses can optimize campaigns in real-time, allocate budget to high-performing channels, and experiment with new strategies to improve results.
3.3 Customer Journey Mapping:
- Marketing analytics helps businesses map the customer journey across multiple touchpoints and channels, from initial awareness to conversion and retention.
- By analyzing customer interactions and behavior at each stage of the journey, businesses can identify friction points, optimize user experience, and create seamless and personalized experiences for customers.
3.4 Performance Measurement and ROI:
- Marketing analytics enables businesses to measure the effectiveness of marketing initiatives and quantify their return on investment (ROI).
- By tracking KPIs such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLV), conversion rates, and revenue attribution, businesses can assess the impact of marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
Conclusion:
Marketing analytics empowers businesses to harness the power of data to make strategic decisions, optimize marketing efforts, and drive business growth. By collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data effectively, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, campaign performance, and market trends, enabling them to stay ahead of the competition and deliver exceptional experiences to their audience.
Comments
Post a Comment