Unveiling Consumer Insights: A Deep Dive into Marketing Research Methods and Understanding Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior lies at the heart of marketing success. Understanding what drives consumers' purchasing decisions, preferences, and behaviors is essential for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies and engage with their target audience successfully. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the diverse methods of marketing research used to unravel consumer behavior, uncover valuable insights, and inform strategic decision-making.
Part 1: Importance of Understanding Consumer Behavior

1.1 Foundation of Marketing Strategy:
- Consumer behavior serves as the foundation upon which marketing strategies are built. By understanding consumer needs, wants, and motivations, businesses can tailor their products, services, and messaging to resonate with their target audience effectively.
1.2 Market Segmentation and Targeting:
- Understanding consumer behavior enables businesses to segment the market based on demographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors and target specific audience segments with tailored marketing efforts.
- Effective segmentation and targeting increase the relevance and effectiveness of marketing campaigns, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
1.3 Product Development and Innovation:
- Consumer insights guide product development and innovation by identifying unmet needs, uncovering pain points, and predicting future trends and preferences.
- By aligning product offerings with consumer demands and preferences, businesses can gain a competitive edge and drive innovation in the marketplace.
Part 2: Marketing Research Methods
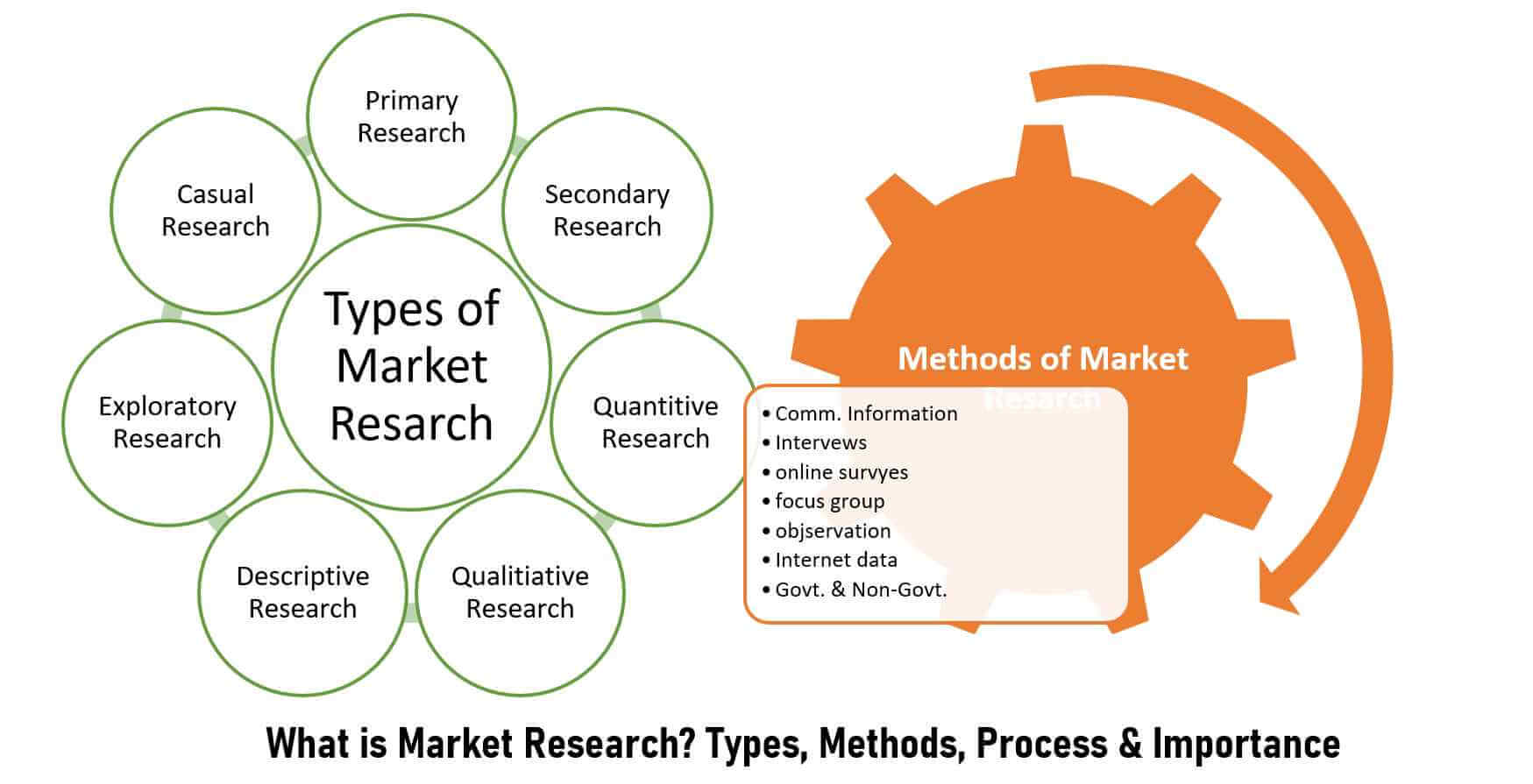
2.1 Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Surveys and questionnaires are widely used to gather quantitative data on consumer attitudes, preferences, and behaviors.
- Online surveys, telephone surveys, and mail surveys are common methods for collecting large-scale data from diverse consumer populations.
2.2 Focus Groups:
- Focus groups involve gathering a small group of participants to engage in guided discussions and provide qualitative insights on specific topics or products.
- Focus groups facilitate in-depth exploration of consumer perceptions, opinions, and attitudes, allowing researchers to uncover underlying motivations and emotions.
2.3 Interviews:
- In-depth interviews involve one-on-one conversations with consumers to explore their experiences, preferences, and behaviors in greater detail.
- Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, over the phone, or through video conferencing, providing researchers with valuable qualitative data and nuanced insights.
2.4 Observational Research:
- Observational research involves directly observing and recording consumer behavior in real-world settings, such as retail stores, websites, or social media platforms.
- Through observation, researchers can gain insights into consumer decision-making processes, product usage patterns, and interactions with brands.
2.5 Data Analytics:
- Data analytics leverages advanced technologies and algorithms to analyze large volumes of structured and unstructured data, such as sales data, website traffic, and social media interactions.
- By mining data for patterns, trends, and correlations, businesses can uncover actionable insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Part 3: Case Study: Coca-Cola's Consumer Research Journey
3.1 Background:
- Coca-Cola, a global leader in the beverage industry, continuously invests in consumer research to stay attuned to evolving consumer preferences and trends.
3.2 Strategy:
- Coca-Cola employs a mix of qualitative and quantitative research methods, including surveys, focus groups, and observational research, to gain comprehensive insights into consumer behavior.
- The company utilizes advanced data analytics tools and techniques to analyze consumer data from various sources, including social media, sales transactions, and market research studies.
3.3 Example:
- Through consumer research, Coca-Cola identified a growing demand for healthier beverage options and shifting preferences towards natural ingredients and reduced sugar content.
- Leveraging these insights, Coca-Cola introduced new product lines, such as Coca-Cola Zero Sugar and Coca-Cola Life, to meet consumer demands and drive growth in the health and wellness segment.
Conclusion:
Understanding consumer behavior is a cornerstone of successful marketing. By employing a variety of research methods, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, motivations, and behaviors, allowing them to develop targeted marketing strategies, innovate products, and build lasting relationships with their target audience. As demonstrated by Coca-Cola's consumer research journey, investing in understanding consumer behavior can lead to strategic decisions that drive business growth and success in today's competitive marketplace.
Comments
Post a Comment