Decoding Pricing Strategies: Mastering the Art of Setting the Right Price for Your Product or Service with Five Exemplary Cases

Pricing is not just about putting a number on your product or service; it's a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business's success. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of pricing strategies, exploring the key principles, methodologies, and real-world examples that showcase the art and science of setting the right price.
Part 1: Understanding Pricing Strategies
1.1 The Importance of Pricing
- Significance of Pricing: Pricing directly influences revenue, profitability, market positioning, and customer perception.
- Role of Pricing Strategies: Strategies guide businesses in determining optimal price points to maximize value capture and competitiveness.
1.2 Factors Influencing Pricing Decisions
- Cost-Based Factors: Considerations such as production costs, overhead expenses, and desired profit margins.
- Demand-Based Factors: Understanding customer demand, price sensitivity, elasticity, and willingness to pay.
- Competitive Factors: Analyzing competitors' pricing strategies, market share, and differentiation.
Part 2: Common Pricing Strategies and Methodologies
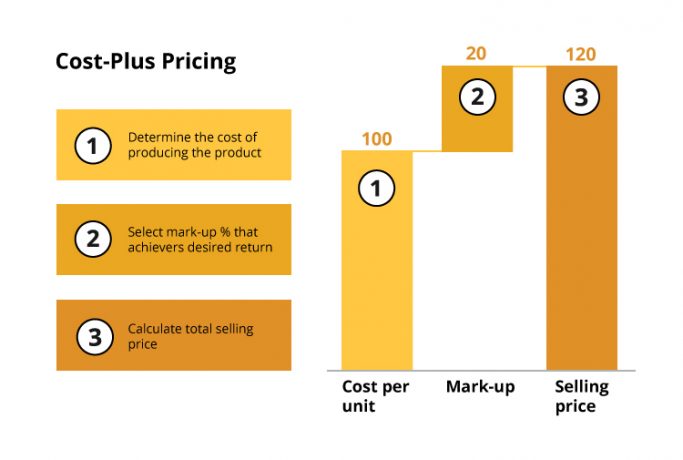
2.1 Cost-Plus Pricing
- Definition: Setting prices based on production costs plus a markup to ensure desired profitability.
- Application: Commonly used in manufacturing and retail industries for straightforward cost recovery and profit generation.
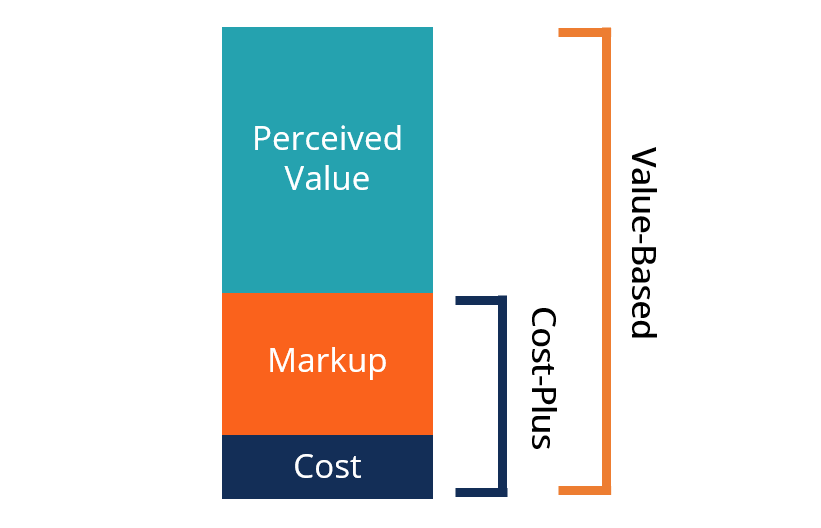
2.2 Value-Based Pricing
- Definition: Determining prices based on the perceived value of the product or service to the customer.
- Application: Suitable for products or services with unique features, superior quality, or significant benefits relative to alternatives.
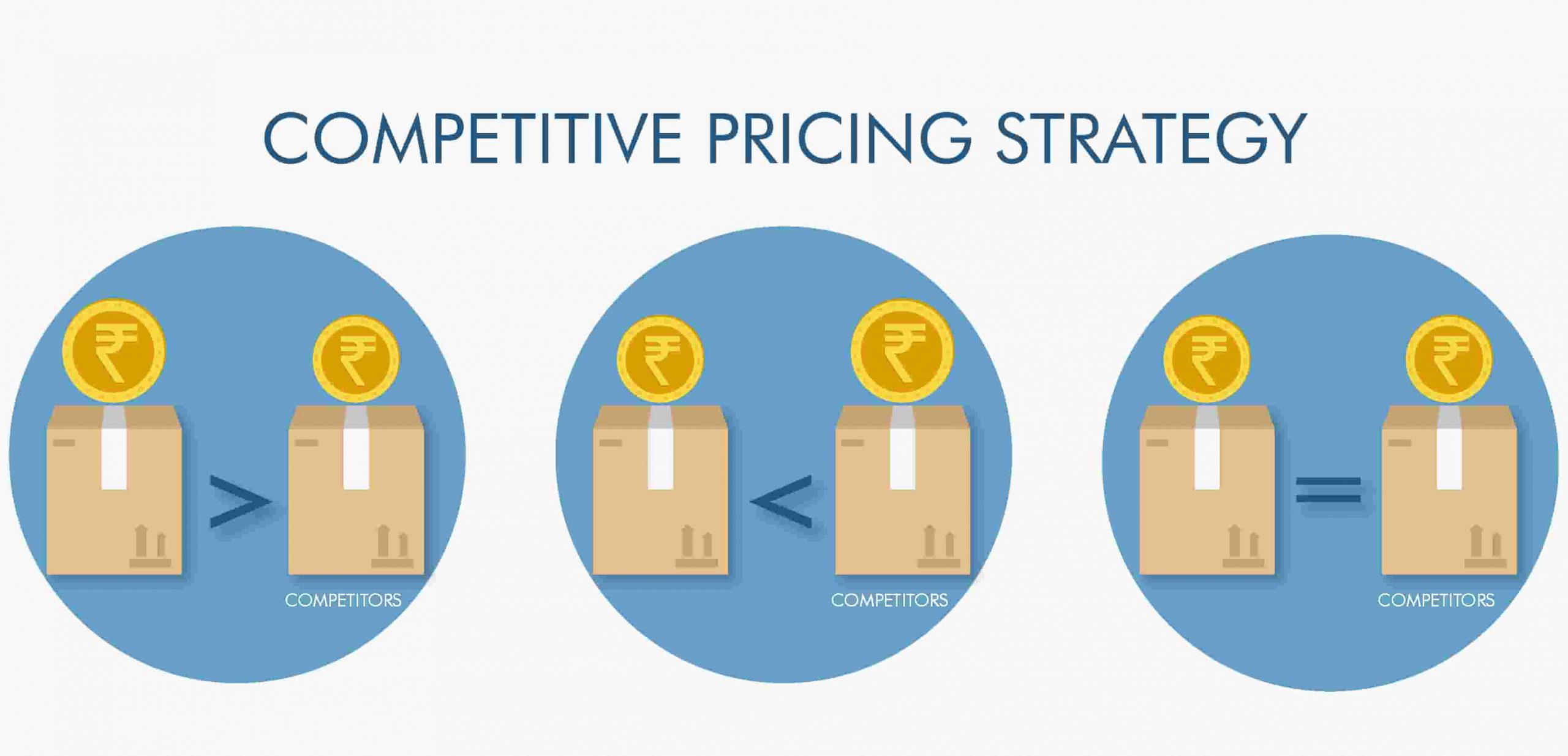
2.3 Competitive Pricing
- Definition: Setting prices based on competitors' prices, positioning the product as cheaper, similar, or premium.
- Application: Often used in saturated markets with intense competition to gain market share or differentiate offerings.

2.4 Dynamic Pricing
- Definition: Adjusting prices in real-time based on factors such as demand fluctuations, supply constraints, and customer behavior.
- Application: Common in e-commerce, travel, and hospitality industries to optimize revenue and manage inventory.

2.5 Psychological Pricing
- Definition: Leveraging psychological principles to influence perceptions of value and willingness to pay.
- Application: Examples include using charm pricing (e.g., $9.99 instead of $10) and decoy pricing (e.g., offering a higher-priced option to make others seem more attractive).
Part 3: Real-World Examples of Effective Pricing Strategies
3.1 Apple Inc. - Premium Pricing for iPhones
- Strategy: Value-Based Pricing
- Approach: Positioning iPhones as high-end, premium products with innovative features and design.
- Impact: Maintaining high profit margins, enhancing brand perception, and fostering customer loyalty among affluent segments.
3.2 Walmart - Everyday Low Prices
- Strategy: Cost-Plus Pricing
- Approach: Offering consistently low prices on a wide range of products, leveraging economies of scale and operational efficiencies.
- Impact: Attracting price-sensitive consumers, driving traffic to stores, and gaining market share in the retail industry.
3.3 Uber - Surge Pricing during Peak Hours
- Strategy: Dynamic Pricing
- Approach: Increasing prices during periods of high demand to incentivize more drivers and balance supply and demand.
- Impact: Maximizing revenue during peak hours, improving service availability, and optimizing driver earnings.
3.4 Netflix - Tiered Pricing for Subscription Plans
- Strategy: Value-Based Pricing
- Approach: Offering different subscription tiers with varying features and pricing to cater to different customer segments.
- Impact: Increasing revenue through upselling and cross-selling, accommodating diverse customer needs and preferences.
3.5 Starbucks - Premium Pricing for Specialty Coffee
- Strategy: Psychological Pricing
- Approach: Charging premium prices for specialty coffee beverages, creating a perception of quality and exclusivity.
- Impact: Building a premium brand image, fostering customer loyalty, and commanding higher margins compared to competitors.
Conclusion:
Pricing is both an art and a science, requiring a deep understanding of market dynamics, customer behavior, and competitive landscape. By adopting the right pricing strategy and methodologies, businesses can maximize value capture, enhance profitability, and achieve sustainable growth. The real-world examples provided in this guide serve as inspiration and guidance for businesses seeking to master the art of setting the right price for their products or services.

Comments
Post a Comment